🔨 Building The Lava Bazaar: A P2P Cross-Chain Asset Checker
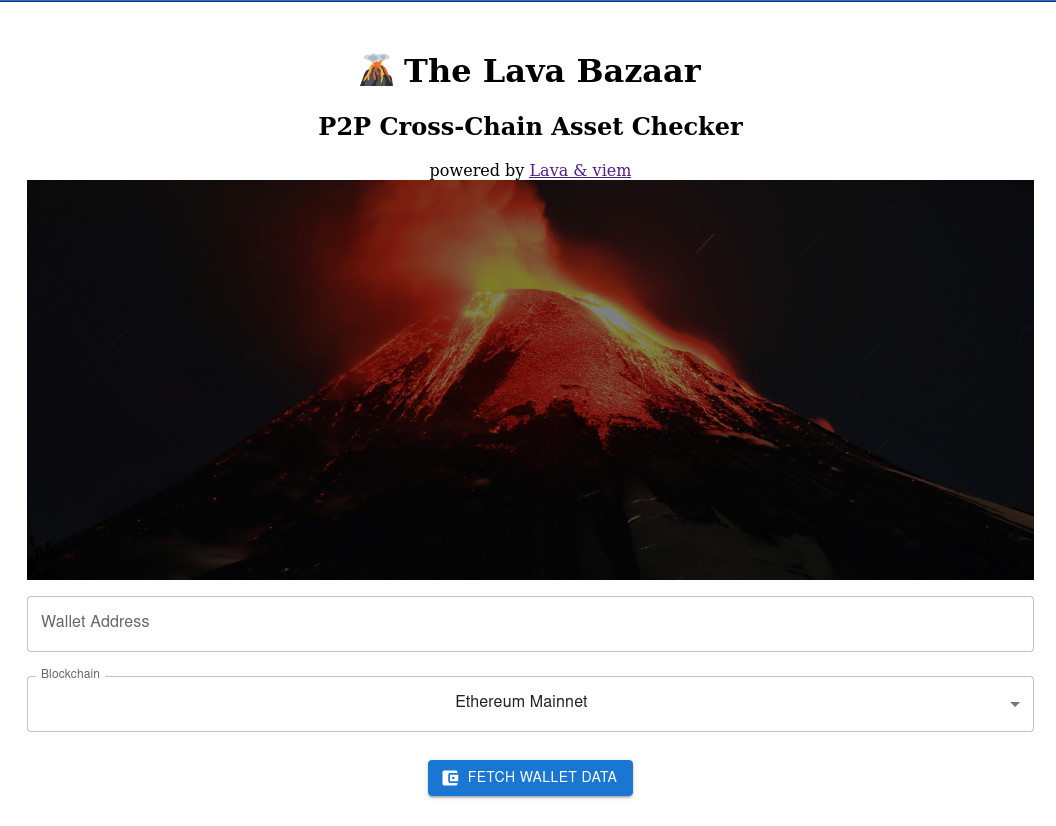
The Lava Bazaar is a simple cross-chain asset checker. It works by leveraging the power of LavaSDK’s P2P RPC integration with viem (lava-viem) to provide users with a React frontend to check wallet balances across different blockchains. Under the hood, Lava replaces viem’s PublicClient with its entire decentralized network of RPC providers providing many benefits for dApp developers. The Lava Bazaar is a basic example that can be modified to interact with any blockchain that is supported by both LavaSDK and viem.
Check out the complete project on Github❗
Overview 🔎
The tutorial explores how to use lava-viem to build a fully decentralized cross-chain asset checker which works across all chains mutually supported by LavaSDK and viem. Being able to check balances across multiple chains with a single credential is a building block to many web3 tools including wallets, indexers, and exchanges.
This tutorial will guide you through creating a simple app that can:
- Fetch and display current wallet balances and transaction counts from Ethereum, Arbitrum, FileCoin, Avalanche, Celo, Optimism, and Polygon mainnets.
- Dynamically add/remove support for new blockchains with the simple editing of two arrays!
- Access P2P RPC on viem without a single RPC URL
Prerequisites 📦
- Basic understanding of Node.js, Express, and React.
- Node.js and npm installed.
- Familiarity with using APIs / routing structures!
Backend Setup 🔙
We'll begin by setting up an Express.js server to interact with the blockchain networks via viem's client instances. In a normal dApp, we wouldn’t need to separate out a backend from a frontend, but due to network conditions at the time of this tutorial - this is a decent setup to avoid CORS issues with certain providers.
📥 Install dependencies
npm install @lavanet/lava-viem express viem
⚒️ Build a Constructor
// viemclient.js
const { createViemClientWithLavaSDK } = require("@lavanet/lava-viem");
const clientList = {};
async function createClientForChain(chainID) {
try {
const client = await createViemClientWithLavaSDK({
badge: {
badgeServerAddress: "https://badges.lavanet.xyz",
projectId: " // ", // Fetch your project ID from https://gateway.lavanet.xyz
},
geolocation: "1", //optional
chainIds: chainID
});
if (client) {
console.log(`${chainID} 🔩 intialized: `, client.name, client.transport.name, client.uid);
return client;
} else {
console.log(`${chainID} ❌ failed to initialize!`);
};
} catch (error) {
console.log(`❗ Error: ${error}`)
};
};
async function getClient(chainID) {
const client = clientList[chainID];
if (!client) {
throw new Error(` Unsupported or unitialized chain: ${chainID}`);
}
return client;
};
module.exports = { createClientForChain, clientList };
In viemclient.js, we define a function to create viem clients for various chains and store them in clientList. We’ll want to export this so that we incorporate this logic in our server. We’ll also write a small async function getClient() which allows us to select which chain to use for a given request! 🧠
🧭 Write Initialization Function
// server.js
const express = require('express');
const { clientList, createClientForChain } = require('./viemclient');
const app = express();
const supportedChains = ["ARB1", "AVAX", "CELO", "ETH1", "FVM", "OPTM", "POLYGON1"];
(async () => {
for (const chain of supportedChains) {
const client = await createClientForChain(chain);
clientList[chain] = client;
}
})();
// ... Define API endpoints such as /api/wallet/balance
In server.js, we import the functions from viemclient.js and use them to initialize clients and set up API endpoints. We pack this away in an anonymous asynchronous function… Later, we’ll put some API endpoints here!
🌐 Create APIs
Before building routes, we need to revisit viemclient.js. We need to add functions that get the latest block number, get the wallet balance of a wallet in question, and get the number of transactions for a given address. All of these will use the getClient() function to determine which instance we will communicate to… In viemclient.js put the following:
//viemclient.js (cont'd)
// Function that gets the latest block from the selected chain!
async function getBlockNumber(chainInput) {
const client = await getClient(chainInput);
//Call the viem getBlockNumber
const latestBlockNumber = await client.getBlockNumber();
//convert to Number
return Number(latestBlockNumber);
}
// Function that gets wallet balance of a given address on a given chain
async function getWalletBalance(addressInput, chainInput) {
const client = await getClient(chainInput);
//Call the viem getBalance
let balance = await client.getBalance({ address: addressInput });
return balance;
};
// Function that gets the number of TXs from a given address!
async function getWalletTxNumber(addressInput, chainInput) {
const client = await getClient(chainInput);
//Call the viem getTxCount
const txCount = await client.getTransactionCount({ address: addressInput });
return txCount;
};
In server.js we’ll need to add some routes, so that these can be called from our frontend without issue. That means our server.js can include something like this:
//server.js (cont'd)
// Middleware to parse JSON bodies
app.use(express.json());
app.get('/api/chain/latest_block_num', async (req, res) => {
console.log("✅ GET - /api/chain/latest_block_num", req.query.chain);
try {
const chain = req.query.chain
const latestBlockNum = await getBlockNumber(chain);
console.log(`➡️ ${chain} Returned BlockNum: ${latestBlockNum}`)
res.json({ chain: chain, latestBlockNumber: latestBlockNum })
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: error.message });
}
})
// Route to get wallet balances
app.get('/api/wallet/balance', async (req, res) => {
console.log("✅ GET - /api/wallet/balance", req.query.address, req.query.chain);
try {
const walletAddress = req.query.address;
const chain = req.query.chain
const balance = await getWalletBalance(walletAddress, chain); // Your function to get the balance
const balanceString = balance.toString();
console.log(`➡️ ${chain} Returned Balance: ${balance} for ${walletAddress}`)
res.json({ chain: chain, address: walletAddress, balance: balanceString });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: error.message });
}
// Logic to interact with blockchain and fetch balance
});
//Route to get Transaction Count
app.get('/api/wallet/transaction_count', async (req, res) => {
console.log("✅ GET - /api/wallet/transaction_count", req.query.address, req.query.chain);
// Logic to interact with blockchain and fetch transactions
try {
const walletAddress = req.query.address;
const chain = req.query.chain;
// Check if all required parameters are provided
if (!walletAddress || !chain) {
return res.status(400).json({ error: 'Missing required parameters' });
};
//Get and return the Transactions
const transactionCount = await getWalletTxNumber(walletAddress, chain);
console.log(`➡️ ${chain} Counted ${transactionCount} TXs on ${walletAddress}`);
res.json({ chain, address: walletAddress, count: transactionCount });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: error.message });
}
});
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`🖥️⚡ Server running on port ${PORT}`);
});
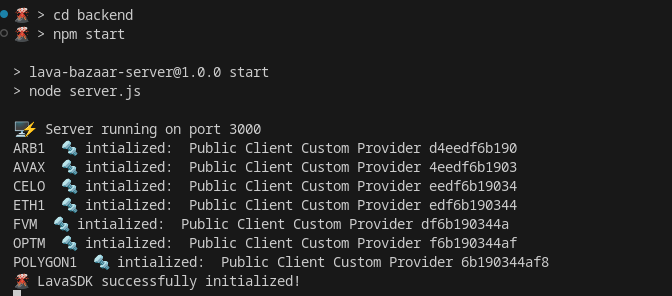
These 3 basic routes will form the basis of our application! Once you have constructed them correctly, go ahead and give them a test with node server.js . We should get something like the following (give or take a few lines ;) ✨
Frontend Setup 🪟
Now, we’re ready to move onto building our interfaces, if you’re familiar with React, this should be a breeze. If not, please ensure that you’ve setup your index.js, index.html , and App.js . We deliberately avoid using create-react-app because of a few configuration issues it has with common web3 dependencies. If you’re not used to it, setting up a React environment without using create-react-app is not trivial! So take your time and consult a separate tutorial or two.
You may use any of these dependencies or more, depending on your setup:
Dependency Tree (
npm ls)├── @babel/[email protected]
├── @babel/[email protected]
├── @babel/[email protected]
├── [email protected]
├── [email protected]
├── [email protected]
├── [email protected]
├── [email protected]
├── [email protected]
├── [email protected]
└── [email protected]
💼 Set up a WalletInfo Component
//WalletInfo.js
function WalletInfo() {
const [address, setAddress] = useState('');
const [chain, setChain] = useState('ETH1');
const [balance, setBalance] = useState('');
const [latestBlock, setLatestBlock] = useState('')
const [txCount, setTxCount] = useState('');
const [error, setError] = useState('');
const chainOptions = {
'ARB1': 'Arbitrum Mainnet',
'AVAX': 'Avalanche Mainnet',
'CELO': 'Celo Mainnet',
'ETH1': 'Ethereum Mainnet',
'FVM': 'FileCoin Mainnet',
'OPTM': 'Optimism Mainnet',
'POLYGON1': 'Polygon Mainnet'
};
const fetchWalletBalance = async () => {
const response = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/wallet/balance?address=${address}&chain=${chain}`);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Error: ${response.statusText}`);
const data = await response.json();
setBalance(data.balance);
};
const fetchCurrentBlock = async () => {
const response = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/chain/latest_block_num?chain=${chain}`)
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Error: ${responseLatestBlock.statusText}`);
const data = await response.json();
setLatestBlock(data.latestBlockNumber);
}
const fetchTransactionCount = async () => {
const response = await fetch(`http://localhost:3000/api/wallet/transaction_count?chain=${chain}&address=${address}`);
if (!response.ok) throw new Error(`Error: ${response.statusText}`);
const data = await response.json();
setTxCount(data.count);
};
const fetchWalletData = async () => {
setError('');
try {
await fetchCurrentBlock();
await fetchWalletBalance();
await fetchTransactionCount();
} catch (err) {
setError(err.message);
}
};
The basic logic of the WalletInfo.js component is above. We have fetch functions that call the APIs we created and grab the proper responses and set state with them; we also outlined our chainOptions for when we build our interface. Each time a button we’ll create is called, we’ll activate each of these functions so as to update the interface, hence fetchWalletData(). Before worrying about all that, we will also need to add a return statement detailing the layout of the component before closing our final bracket!
//WalletInfo.js (cont'd)
return (
<div style={{ padding: '20px' }}>
<center><h1>🌋 The Lava Bazaar</h1>
<h2>P2P Cross-Chain Asset Checker</h2>
powered by <a href='https://docs.lavanet.xyz/viem'>Lava & viem</a>
<div style={{ marginBottom: '20px' }}>
<TextField
label="Wallet Address"
value={address}
onChange={(e) => setAddress(e.target.value)}
variant="outlined"
fullWidth
margin="normal"
/>
<FormControl fullWidth margin="normal">
<InputLabel>Blockchain</InputLabel>
<Select
value={chain}
onChange={(e) => setChain(e.target.value)}
label="Blockchain"
>
{Object.entries(chainOptions).map(([value, label]) => (
<MenuItem key={value} value={value}>
{label}
</MenuItem>
))}
</Select>
</FormControl>
<Button
variant="contained"
color="primary"
onClick={fetchWalletData}
style={{ marginTop: '20px' }}
>
Fetch Wallet Data
</Button>
</div>
{balance && <p>Balance: {balance}</p>}
{txCount && <p>TxCount: {txCount}</p>}
{latestBlock && <p>Latest Block: {latestBlock}</p>}
{error && <p style={{ color: 'red' }}>Error: {error}</p>}
</center>
</div>
);
}
// Now we can export!
export default WalletInfo;
And we have a complete UI! Let’s be sure to add it to the App.js main App() function:
//App.js
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<WalletInfo />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
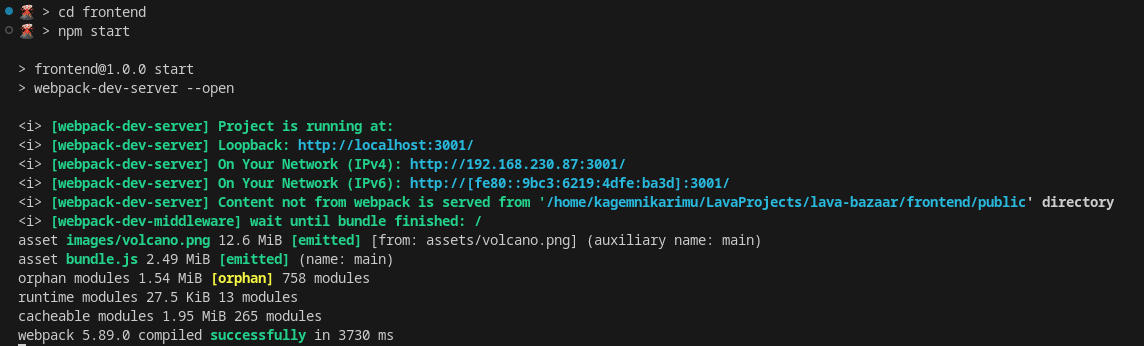
Once you’re certain you’ve plugged up all the holes in your frontend - go ahead and give your new Lava Bazaar application a spin with npm start command. if all is well, you should get output similar to the following:
Test your might! 🗳️
Give it a test! Does it work? Take a look at a final version here!
https://github.com/KagemniKarimu/lava-bazaar
Challenges 🧩
Need a way to turn up the difficulty? Want to practice your web3 dev skills and learn more about the integration? Try the following:
- ⛓️Add support for more chains
- 🦜Parse the Balances to Make Them more Human Readable
- 📏Add Validation for Address Input(s)
- 🕐Implement Real-Time Balance Watching
- 💾Cache Responses for More Speed
- 🔃Parallelize the Initialization Process for all Chains
- 🔎 Add Tx LookUp in Addition to Address Lookup on the same Text Input